Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) is a critical component in the electronic manufacturing industry. As technology advances, so does the complexity and capability of PCBAs, driving innovation and efficiency in the production of electronic devices. This article delves into the technology of PCBA, highlighting its significance, processes, and recent advancements in the electronic field.
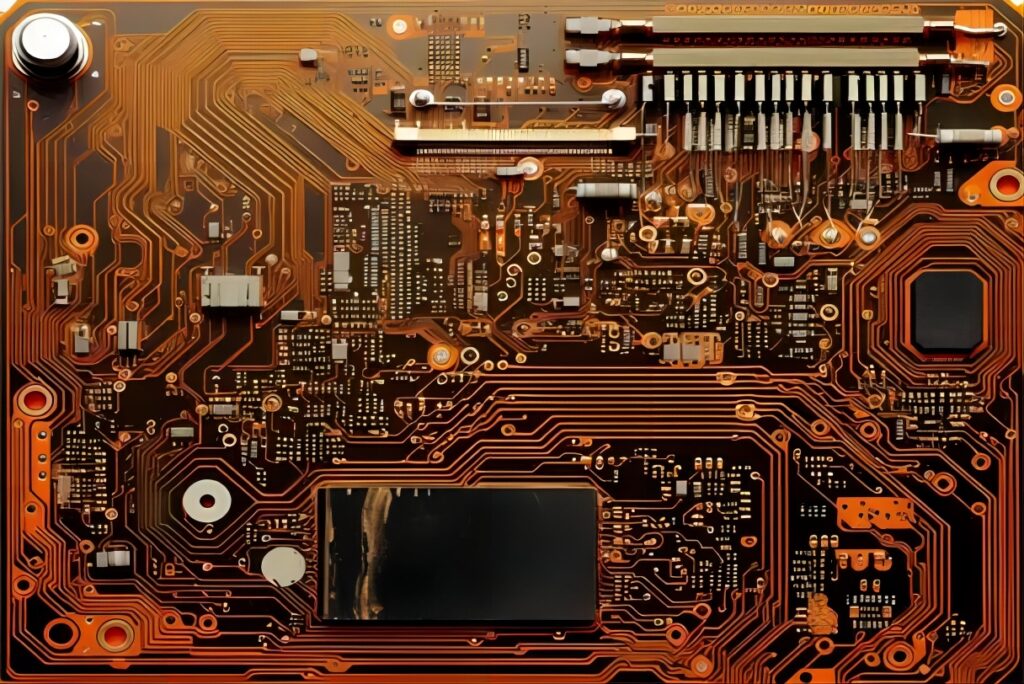
What is PCBA?
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly, which involves the process of mounting electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB). The PCB provides the foundation and interconnections for the components, enabling them to function as a cohesive unit. PCBA is essential in the creation of various electronic devices, from simple household gadgets to complex industrial machinery.
Key Components of PCBA
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB):The substrate that holds and connects electronic components.
- Electronic Components:These include resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), and more.
- Soldering Material:Typically solder paste or wire, used to attach components to the PCB.
PCBA Process Overview
1.Design and Layout:
– The process begins with designing the PCB layout, which involves placing components and creating electrical pathways.
– Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is often used to ensure precision and optimize the layout for performance and manufacturability.
2.rinting and Etching:
– The designed PCB layout is printed onto a copper-clad board.
– The board undergoes an etching process to remove excess copper, leaving behind the desired circuit patterns.
3.Component Placement:
– Electronic components are placed onto the PCB using automated pick-and-place machines.
– Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is commonly used, allowing for high-speed and accurate component placement.
4.Soldering:
– The components are soldered onto the PCB using techniques like reflow soldering (for SMT) or wave soldering (for through-hole components).
– Proper soldering ensures reliable electrical connections and mechanical stability.
5.Inspection and Testing:
– Assembled boards undergo rigorous inspection and testing to identify any defects or issues.
– Techniques such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection, and functional testing are employed.
Advancements in PCBA Technology
1.Miniaturization and High Density:
– Advances in SMT and component packaging have enabled the production of smaller and more densely packed PCBAs.
– This is crucial for modern devices like smartphones, wearables, and IoT gadgets.
2.Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBs:
– Flexible PCBs, made from flexible substrates, allow for bending and folding, offering new design possibilities.
– Rigid-flex PCBs combine rigid and flexible sections, providing durability and versatility in complex applications.
3.Lead-Free Soldering:
– Environmental regulations have driven the adoption of lead-free soldering processes.
– Lead-free solder materials, such as tin-silver-copper (SAC) alloys, are now widely used to ensure compliance and reduce environmental impact.
4.Automated Assembly and Industry 4.0:
– Automation and Industry 4.0 technologies have revolutionized PCBA manufacturing.
– Smart factories, equipped with robotics, IoT devices, and AI-driven analytics, enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and enable real-time monitoring.
5.Advanced Testing and Quality Control:
– Improved testing methods, including in-circuit testing (ICT) and boundary scan testing, ensure higher reliability and performance.
– Advanced inspection systems provide detailed analysis and fault detection, minimizing defects and improving overall quality.
Conclusion
The technology of PCBA is constantly evolving, driven by the demand for more compact, powerful, and reliable electronic devices. From innovative design techniques to advanced manufacturing processes, the advancements in PCBA technology are shaping the future of the electronic field. As the industry continues to progress, we can expect even more breakthroughs that will further enhance the capabilities and applications of PCBA in electronics.
