In the realm of electronics, Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) stands as a crucial step in transforming bare circuit boards into functional electronic devices. This intricate process involves meticulously placing and soldering various electronic components onto a PCB, breathing life into the intricate circuitry that powers a wide range of products.
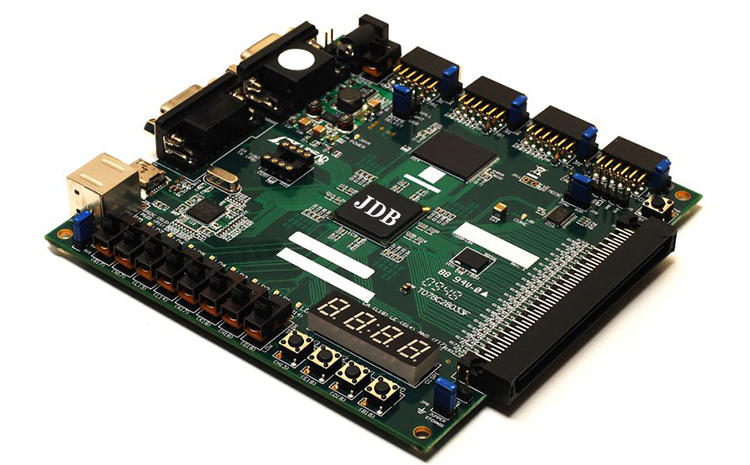
Understanding PCBA: The Essence
A PCB serves as the foundation for electronic components, providing a structured platform for interconnecting them. However, a PCB alone is incomplete; it’s the PCBA process that brings the board to life. This comprehensive procedure encompasses:
Component Placement: Each electronic component, ranging from tiny resistors to complex integrated circuits, is precisely positioned onto the designated locations on the PCB.
Soldering: Solder, a fusible metal alloy, is skillfully applied to connect the components to the copper traces on the PCB, forming durable electrical pathways.
Inspection: Rigorous quality control checks are implemented throughout the PCBA process to ensure the accuracy of component placement, solder joints, and overall functionality.
Types of PCBA Techniques
The PCBA process can be executed using various techniques, each tailored to specific applications and component types:
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT): SMT is widely employed for smaller, lightweight components that are mounted directly onto the PCB surface.
Through-Hole Technology (THT): THT involves inserting component leads through holes drilled in the PCB and soldering them to the bottom side.
Mixed Technology (SMT/THT): This hybrid approach combines SMT and THT, suitable for PCBs with a mix of component sizes and types.
Benefits of PCBA: Unleashing the Power of Electronics
PCBA offers a multitude of advantages that make it indispensable in the electronics industry:
Miniaturization and High Density: PCBA enables the creation of compact electronic devices by packing numerous components onto a single PCB.
Reliability and Durability: The soldering process ensures strong and durable connections, enhancing the longevity of electronic products.
Cost-Effectiveness: Automated PCBA processes streamline production, lowering manufacturing costs and improving efficiency.
Scalability: PCBA can seamlessly adapt to high-volume production, catering to the demands of mass-produced electronics.
Applications of PCBA: Spanning Industries
The versatility of PCBA extends its reach across a diverse range of industries:
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other consumer gadgets rely heavily on PCBA.
Automotive Electronics: PCBA plays a critical role in automotive systems, including engine control units, safety features, and infotainment systems.
Medical Devices: PCBA is essential for medical devices like pacemakers, defibrillators, and diagnostic equipment.
Industrial Automation: PCBA powers industrial control systems, robots, and other automation machinery.
Aerospace and Defense: PCBA is crucial for avionics, navigation systems, and military equipment.
Conclusion: The Driving Force Behind Electronics
PCBA serves as the cornerstone of modern electronics, transforming bare PCBs into functional devices that power our world. Its ability to miniaturize, optimize, and enhance electronic products makes it an indispensable process in the ever-evolving realm of technology. As the demand for sophisticated electronics continues to rise, PCBA will remain at the forefront, driving innovation and shaping the future of electronics.
